ISO 17025 Accredited Laboratories
Solutions for ISO 17025 accredited laboratories – providing accreditation support and statistical tools for evaluation of method validation, uncertainties, and control charts.
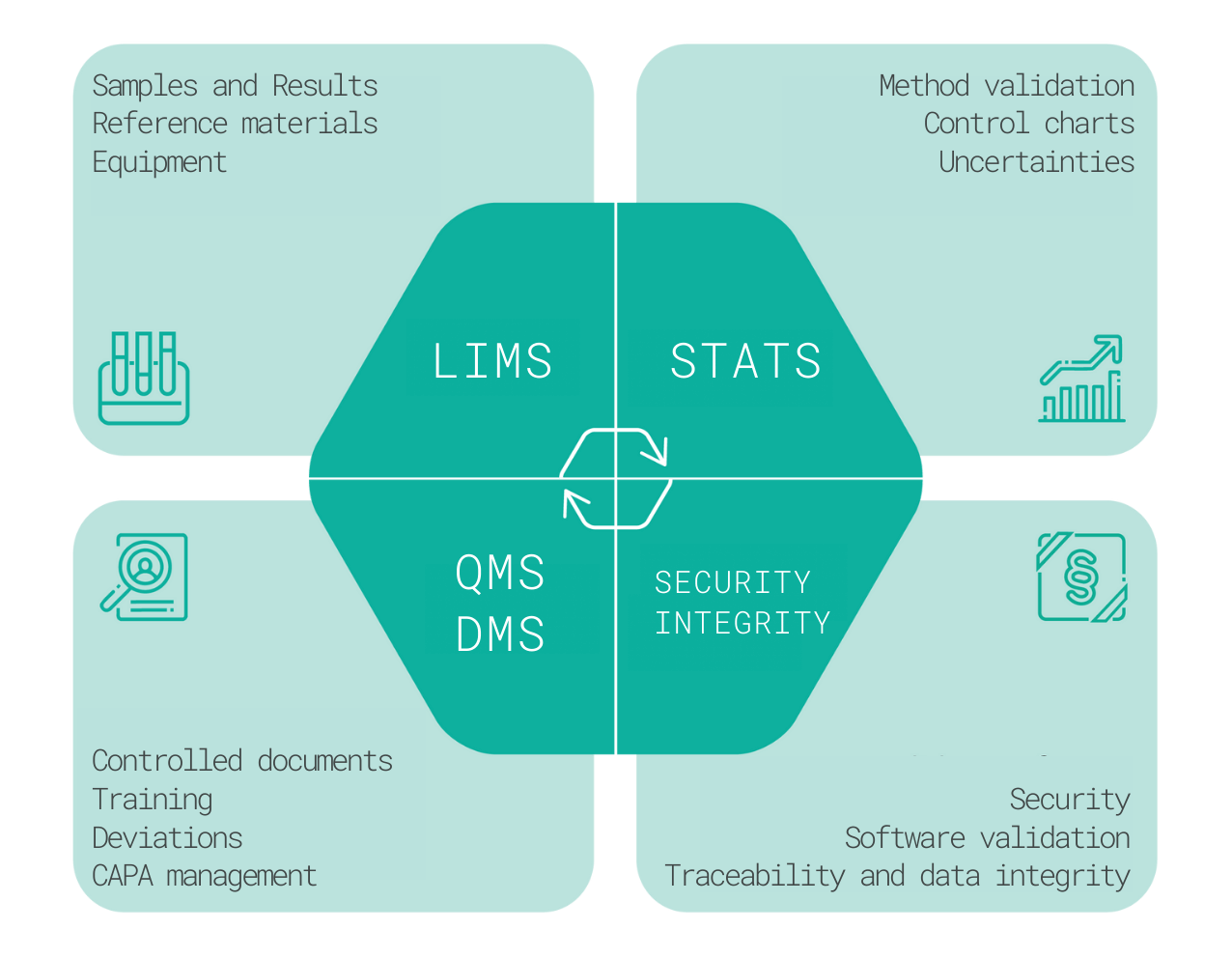
Characteristics and functions
The software was developed in compliance with the requirements of ISO 17025 including art. 7.11, harmonized GMP requirements including US FDA 21 CFR Part 210 and 211, Volume 4 of EU GMP, Supplement 11 (Annex 11), 21 CFR Part 11, and in line with GAMP 5 for the validation of computerized systems.
The LIMS is used to manage the processes in the laboratory and keep related quality records. The basic process is the testing of samples or batches, recording of results, and comparing them with specifications. This process consists of the sample receipt, testing, and results entry, sample inspection, approval, and reporting. This is preceded by the creation of specifications and the development and validation of test methods, which are also recorded, managed, and evaluated through the LIMS. The same applies to equipment registration and calibration management, to reference materials certification and validity monitoring, and to the registration of chemicals, solutions, chromatographic columns, and auxiliary materials.
The LIMS modules also enables effective planning, recording, and evaluation of stability studies, recording of environmental monitoring data and data from supporting systems. It can work with barcodes, QR codes, and supports managerial reporting.
We are currently developing the connection of LIMS with different types of equipment and ERP systems.
The QMS modules can be used for record keeping and quality management of the control laboratory or an entire pharmaceutical company. The scope includes the record and evaluating deviations, the change management process, audits and observations, CAPA management (corrective and preventive actions, investigation of Out-of-Specification (OOS) and Out-of-trend (OOT) results, complaint handling and risk management.
Workflows are configured to match customer requirements and processes, and can use email notifications, task assignments, escalation, and other general functionalities, including managerial reporting.
Document management and training is an integral part of the entire Quality Management System. It can include the complete process from the document creation, review, approval, to activation/release, periodic revisions, archiving, or document cancellation.
The training management is linked to the documentation, starting with the creation of Tests, test questions and the definition of the correct answers, enabling recording and evaluating user answers, quantifying the test score, initiating re-testing if not successful, monitoring the training deadlines, documenting complete and in-complete training, and reminding and escalating missing trainings.
For Document Management and Training, workflows can be configured according to customer requirements and processes, and can use email notifications, task assignments, escalation, and other general functionalities, including managerial reporting.
Statistical Data Evaluation can be done either in LIMS via the Methods or Samples modules, or configured individually. The assessment typically includes evaluation of method validation data, estimation of uncertainties of test results, development and use of control charts, creation and use of calibration models and evaluation of inter-laboratory comparisons.
If there are multiple options for statistical evaluation, all options are included. E.g. for a correct evaluation of Accuracy, it offers a t-test and regression; for linearity, there is the correlation coefficient calculation, ANOVA, or a Sign test. The output of the statistical data evaluation is a numerical result, a graph, and an automatically generated report.
ISO17025 requirements covered by EffiChem 5.0
| ISO 17025 | Requirement | EffiChem module |
| 6.4 | Equipment | Equipment |
| 6.4.13 | Records shall be retained for equipment which can influence laboratory activities. The records shall include the following, where applicable: | Equipment |
| 7.2 | Selection and verification of methods | Methods
> Method validation |
| 7.2.1.3 | The laboratory shall ensure that it uses the latest valid version of a method unless it is not appropriate or possible to do so. | Methods
> Method validation |
| 7.2.1.5 | The laboratory shall verify that it can properly perform methods before introducing them by ensuring that it can achieve the required performance. Records of the verification shall be retained. | Methods
> Method validation |
| 7.2.2 | Validation of methods | Methods
> Method validation |
| 7.2.2.1 | The laboratory shall validate non-standard methods, laboratory-developed methods and standard methods used outside their intended scope or otherwise modified. The validation shall be as extensive as is necessary to meet the needs of the given application or field of application.
… NOTE 2 The techniques used for method validation can be one of, or a combination of, the following: a) calibration or evaluation of bias and precision using reference standards or reference materials; b) systematic assessment of the factors influencing the result; c) testing method robustness through variation of controlled parameters, such as incubator temperature, volume dispensed; d) comparison of results achieved with other validated methods; e) interlaboratory comparisons; f) evaluation of measurement uncertainty of the results based on an understanding of the theoretical principles of the method and practical experience of the performance of the sampling or test method. |
Methods
> Method validation > Accuracy and Precision > Robustness > Inter-laboratory comparison > Uncertainties from Partial uncertainties or Uncertainties form Precision evaluation of from Control charts |
| 7.2.2.2 | When changes are made to a validated method, the influence of such changes shall be determined and where they are found to affect the original validation, a new method validation shall be performed. | Methods
> Method validation > Revalidation after a change, with a full Audit trail and History |
| 7.2.2.3 | The performance characteristics of validated methods, as assessed for the intended use, shall be relevant to the customers’ needs and consistent with specified requirements.
NOTE Performance characteristics can include, but are not limited to, measurement range, accuracy, measurement uncertainty of the results, limit of detection, limit of quantification, selectivity of the method, linearity, repeatability or reproducibility, robustness against external influences or cross-sensitivity against interference from the matrix of the sample or test object, and bias. |
Methods
> Method validation > Range > Uncertainty > Precision > Limit of detection > Limit of Quantification > Selectivity > Linearity > Robustness > Accuracy (Bias) |
| 7.2.2.4 | The laboratory shall retain the following records of validation:
a) the validation procedure used; b) specification of the requirements; c) determination of the performance characteristics of the method; d) results obtained; e) a statement on the validity of the method, detailing its fitness for the intended use. |
Methods
> Method validation Validatiom procedure Acceptance criteria Algorithms and characteristics Results Statement of validity |
| 7.5 | Technical records | |
| 7.5.1 | The laboratory shall ensure that technical records for each laboratory activity contain the results, report and sufficient information to facilitate, if possible, identification of factors affecting the measurement result and its associated measurement uncertainty and enable the repetition of the laboratory activity under conditions as close as possible to the original. The technical records shall include the date and the identity of personnel responsible for each laboratory activity and for checking data and results. Original observations, data and calculations shall be recorded at the time they are made and shall be identifiable with the specific task. | Samples
> Results Primary records |
| 7.5.2 | The laboratory shall ensure that amendments to technical records can be tracked to previous versions or to original observations. Both the original and amended data and files shall be retained, including the date | Audit trail and History of records |
| 7.6 | Evaluation of measurement uncertainty | Methods
> Uncertainty estimation |
| 7.6.1 | Laboratories shall identify the contributions to measurement uncertainty. When evaluating measurement uncertainty, all contributions that are of significance, including those arising from sampling, shall be taken into account using appropriate methods of analysis. | Methods
> Uncertainty estimation > Partial uncertainties |
| 7.6.2 | A laboratory performing calibrations, including of its own equipment, shall evaluate the measurement uncertainty for all calibrations. | Methods
> Uncertainty estimation |
| 7.6.3 | A laboratory performing testing shall evaluate measurement uncertainty. Where the test method precludes rigorous evaluation of measurement uncertainty, an estimation shall be made based on an understanding of the theoretical principles or practical experience of the performance of the method.
NOTE 1 In those cases where a well-recognized test method specifies limits to the values of the major sources of measurement uncertainty and specifies the form of presentation of the calculated results, the laboratory is considered to have satisfied 7.6.3 by following the test method and reporting instructions. NOTE 2 For a particular method where the measurement uncertainty of the results has been established and verified, there is no need to evaluate measurement uncertainty for each result if the laboratory can demonstrate that the identified critical influencing factors are under control. |
Methods
> Uncertainty estimation > Partial uncertainties or from > Precision data or from > Control charts |
| 7.7 | Ensuring the validity of results | Control charts |
| 7.7.1 | The laboratory shall have a procedure for monitoring the validity of results. The resulting data shall be recorded in such a way that trends are detectable and, where practicable, statistical techniques shall be applied to review the results. | Control charts |
| 7.7.2 | The laboratory shall monitor its performance by comparison with results of other laboratories, where available and appropriate. This monitoring shall be planned and reviewed and shall include, but not be limited to, either or both of the following: | Methods > Inter-laboratory comparison |
| 7.8 | Reporting of results | Samples |
| 7.9 | Complaints | Complaints |
| 7.10 | Nonconforming work | Non-confirming work or Out-of-Specification |
| 7.11 | Control of data and information management | Software validation and data integrity |
| 7.11.1 | The laboratory shall have access to the data and information needed to perform laboratory activities. | Software security
> Access control |
| 7.11.2 | The laboratory information management system(s) used for the collection, processing, recording, reporting, storage or retrieval of data shall be validated for functionality, including the proper functioning of interfaces within the laboratory information management system(s) by the laboratory before introduction. Whenever there are any changes, including laboratory software configuration or modifications to commercial off-the-shelf software, they shall be authorized, documented and validated before implementation.
NOTE 1 In this document “laboratory information management system(s)” includes the management of data and information contained in both computerized and non-computerized systems. Some of the requirements can be more applicable to computerized systems than to non-computerized systems. NOTE 2 Commercial off-the-shelf software in general use within its designed application range can be considered to be sufficiently validated. |
Software validation and data integrity |
| 7.11.3 | The laboratory information management system(s) shall:
a) be protected from unauthorized access; b) be safeguarded against tampering and loss; c) be operated in an environment that complies with provider or laboratory specifications or, in the case of non-computerized systems, provides conditions which safeguard the accuracy of manual recording and transcription; d) be maintained in a manner that ensures the integrity of the data and information; e) include recording system failures and the appropriate immediate and corrective actions. |
Software validation and security
> Access control |
| 7.11.4 | When a laboratory information management system is managed and maintained off-site or through an external provider, the laboratory shall ensure that the provider or operator of the system complies with all applicable requirements of this document. | Software validation and vendor qualification |
| 7.11.5 | The laboratory shall ensure that instructions, manuals and reference data relevant to the laboratory information management system(s) are made readily available to personnel. | LIMS documentation |
| 7.11.6 | Calculations and data transfers shall be checked in an appropriate and systematic manner. | Audit rail and History of records |
| 8 | Management system requirements | Controlled documents |
| 8.2 | Management system documentation (Option A) | Controlled documents |
| 8.3 | Control of management system documents (Option A) | Controlled documents |
| 8.4 | Control of records (Option A) | Controlled documents and records |
| 8.5 | Actions to address risks and opportunities (Option A) | Risk analysis and Risk assessment |
| 8.6 | Improvement (Option A) | Improvement |
| 8.7 | Corrective actions (Option A) | CAPA |
| 8.8 | Internal audits (Option A) | Internal audits |
| 8.9 | Management reviews (Option A) | LIMS reporting functionalities |
Customer project support
EffiValidation 4.0



